This vignette shows how some of the tidyverse verbs can be used on
stars objects.
The stars and tidyverse packages are loaded
by
library(stars)
## Loading required package: abind
## Loading required package: sf
## Linking to GEOS 3.12.1, GDAL 3.8.4, PROJ 9.4.0; sf_use_s2() is TRUE
library(dplyr)
##
## Attaching package: 'dplyr'
## The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
##
## filter, lag
## The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
##
## intersect, setdiff, setequal, unionMethods now available for class stars are
methods(class = "stars")
## [1] [ [[<- [<- %in%
## [5] $<- adrop aggregate aperm
## [9] as_tibble as.data.frame as.Date as.POSIXct
## [13] c coerce contour cut
## [17] dim dimnames dimnames<- droplevels
## [21] expand_dimensions filter hist image
## [25] initialize is.na Math merge
## [29] mutate Ops plot prcomp
## [33] predict print pull rename
## [37] select show slice slotsFromS3
## [41] split st_apply st_area st_as_sf
## [45] st_as_sfc st_as_stars st_bbox st_coordinates
## [49] st_crop st_crs st_crs<- st_dimensions
## [53] st_dimensions<- st_downsample st_extract st_geometry
## [57] st_geotransform st_geotransform<- st_interpolate_aw st_intersects
## [61] st_join st_mosaic st_normalize st_redimension
## [65] st_rotate st_sample st_set_bbox st_transform
## [69] st_write time transmute write_stars
## see '?methods' for accessing help and source codeWe will work with a three-band section of a landsat image:
system.file("tif/L7_ETMs.tif", package = "stars") %>%
read_stars -> x
x
## stars object with 3 dimensions and 1 attribute
## attribute(s):
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## L7_ETMs.tif 1 54 69 68.91242 86 255
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta refsys point x/y
## x 1 349 288776 28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [x]
## y 1 352 9120761 -28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [y]
## band 1 6 NA NA NA NA
slice
slice slices a sub-array out of the cube; this is done
by specifying the dimension on which to act, and the slice number.
x %>% slice(band, 6) -> x6
x6
## stars object with 2 dimensions and 1 attribute
## attribute(s):
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## L7_ETMs.tif 1 32 60 59.97521 88 255
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta refsys point x/y
## x 1 349 288776 28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [x]
## y 1 352 9120761 -28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [y]It returns a lower-dimensional array if a single element is selected along the slice dimension.
filter
Similar to slice, filter selects on
dimensions but evaluates their values rather than their index: in
x %>% filter(x > 289000, x < 291000, band > 3) -> x7
x7
## stars object with 3 dimensions and 1 attribute
## attribute(s):
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## L7_ETMs.tif 5 54 70 71.79194 88 252
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta refsys point x/y
## x 1 70 289004 28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [x]
## y 1 352 9120761 -28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [y]
## band 1 3 4 1 NA NAthe subarray is created based on the x coordinate values.
Note that filter converts the object to a
tbl_cube, and uses the dplyr
filter method for tbl_cube objects. This has
the limitation that stars objects with rectilinear,
curvilinear or simple feature geometries cannot be handled. For such
objects, using regular [ selection or using
st_crop may be an alternative.
mutate
x %>% mutate(band2 = 2 * L7_ETMs.tif) -> x2
x2
## stars object with 3 dimensions and 2 attributes
## attribute(s):
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## L7_ETMs.tif 1 54 69 68.91242 86 255
## band2 2 108 138 137.82484 172 510
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta refsys point x/y
## x 1 349 288776 28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [x]
## y 1 352 9120761 -28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [y]
## band 1 6 NA NA NA NA
select
select selects an attribute, or a set of attributes:
x2 %>% select(band2) -> x9
x9
## stars object with 3 dimensions and 1 attribute
## attribute(s):
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## band2 2 108 138 137.8248 172 510
## dimension(s):
## from to offset delta refsys point x/y
## x 1 349 288776 28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [x]
## y 1 352 9120761 -28.5 SIRGAS 2000 / UTM zone 25S FALSE [y]
## band 1 6 NA NA NA NA
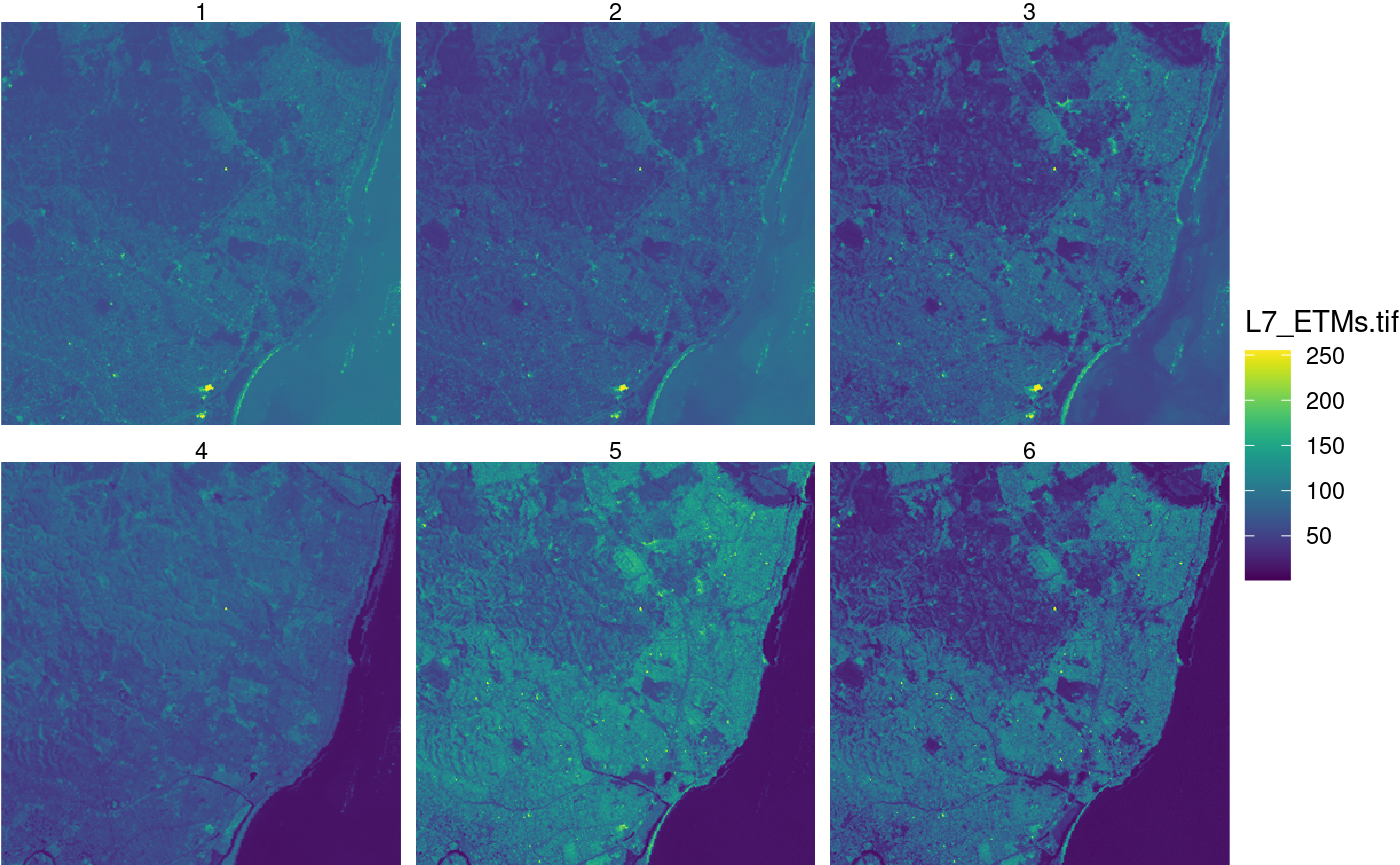
geom_stars
geom_raster is a ggplot2 geom function that
accepts stars objects as its data argument
and
- sets up the raster or vector spatial coordinates as plot dimensions, and the first attribute as the fill variable
- allows for downsampling (without choosing a suitable downsampling level)
- chooses between using
geom_raster,geom_rectandgeom_sfdepending on whether the geometry is regular, rectilinear or has vector geometries
An example use is
library(ggplot2)
library(viridis)
## Loading required package: viridisLite
ggplot() +
geom_stars(data = x) +
coord_equal() +
facet_wrap(~band) +
theme_void() +
scale_fill_viridis() +
scale_x_discrete(expand = c(0, 0)) +
scale_y_discrete(expand = c(0, 0))