Neighbours list from knn object
knn2nb.RdThe function converts a knn object returned by knearneigh
into a neighbours list of class nb with a list of integer vectors
containing neighbour region number ids.
Value
The function returns an object of class nb with a list of integer vectors containing neighbour region number ids. See card for details of “nb” objects.
Author
Roger Bivand Roger.Bivand@nhh.no
Examples
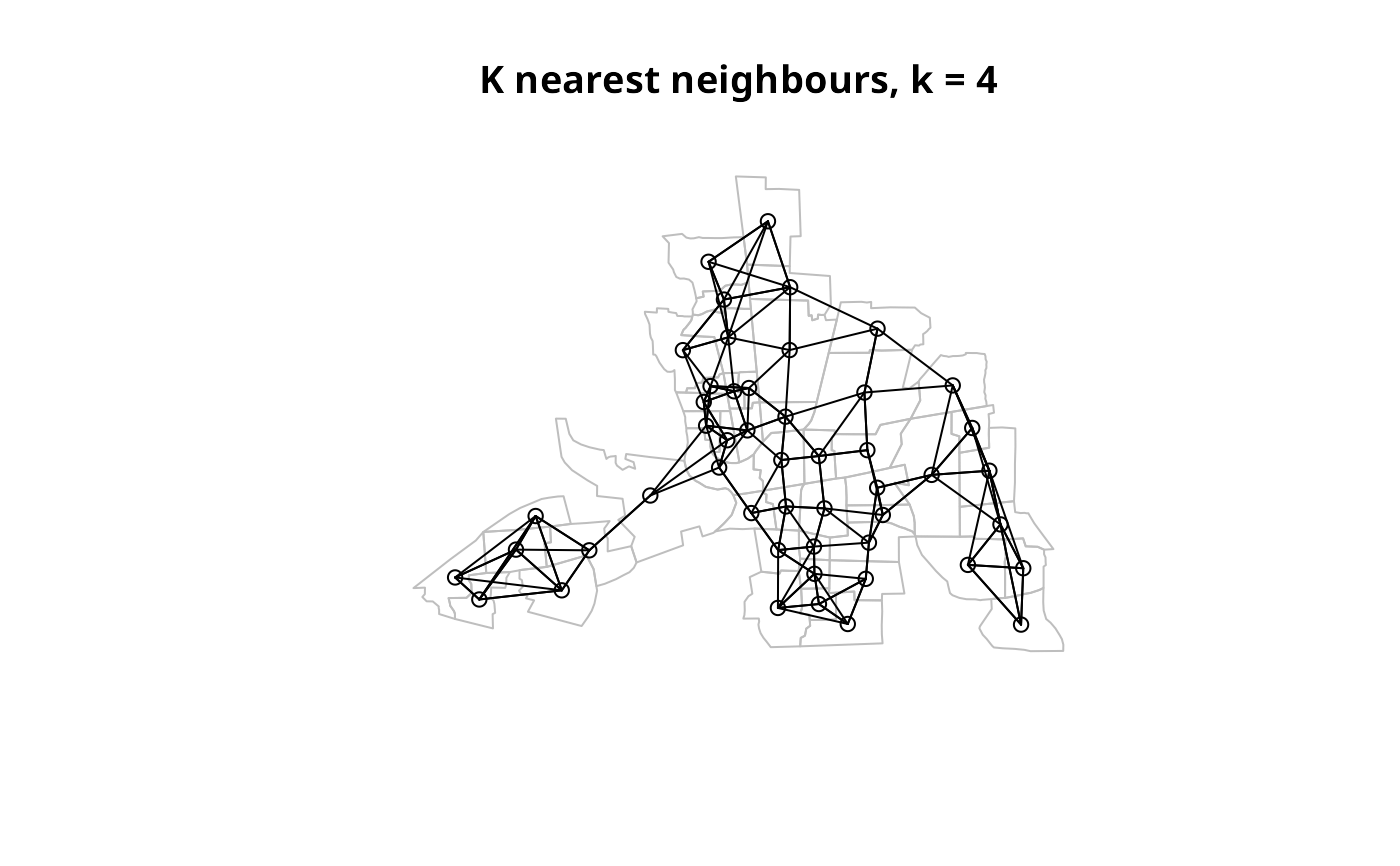
columbus <- st_read(system.file("shapes/columbus.gpkg", package="spData")[1], quiet=TRUE)
coords <- st_coordinates(st_centroid(columbus))
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
col.knn <- knearneigh(coords, k=4)
plot(st_geometry(columbus), border="grey")
plot(knn2nb(col.knn), coords, add=TRUE)
title(main="K nearest neighbours, k = 4")
 # example of reading points with readr::read_csv() yielding a tibble
load(system.file("etc/misc/coords.rda", package="spdep"))
class(coords)
#> [1] "spec_tbl_df" "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"
knn2nb(knearneigh(coords, k=4))
#> Neighbour list object:
#> Number of regions: 100
#> Number of nonzero links: 400
#> Percentage nonzero weights: 4
#> Average number of links: 4
#> Non-symmetric neighbours list
# example of reading points with readr::read_csv() yielding a tibble
load(system.file("etc/misc/coords.rda", package="spdep"))
class(coords)
#> [1] "spec_tbl_df" "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"
knn2nb(knearneigh(coords, k=4))
#> Neighbour list object:
#> Number of regions: 100
#> Number of nonzero links: 400
#> Percentage nonzero weights: 4
#> Average number of links: 4
#> Non-symmetric neighbours list