Areal-weighted interpolation of polygon data
Usage
st_interpolate_aw(x, to, extensive, ...)
# S3 method for class 'sf'
st_interpolate_aw(x, to, extensive, ..., keep_NA = FALSE, na.rm = FALSE)Arguments
- x
object of class
sf, for which we want to aggregate attributes- to
object of class
sforsfc, with the target geometries- extensive
logical; if TRUE, the attribute variables are assumed to be spatially extensive (like population) and the sum is preserved, otherwise, spatially intensive (like population density) and the mean is preserved.
- ...
ignored
- keep_NA
logical; if
TRUE, return all features into, ifFALSEreturn only those with non-NA values (but withrow.namesthe index corresponding to the feature into)- na.rm
logical; if
TRUEremove features withNAattributes fromxbefore interpolating
Details
if extensive is TRUE and na.rm is set to TRUE, geometries with NA are effectively treated as having zero attribute values.
Examples
nc = st_read(system.file("shape/nc.shp", package="sf"))
#> Reading layer `nc' from data source
#> `/home/runner/work/_temp/Library/sf/shape/nc.shp' using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
#> Simple feature collection with 100 features and 14 fields
#> Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -84.32385 ymin: 33.88199 xmax: -75.45698 ymax: 36.58965
#> Geodetic CRS: NAD27
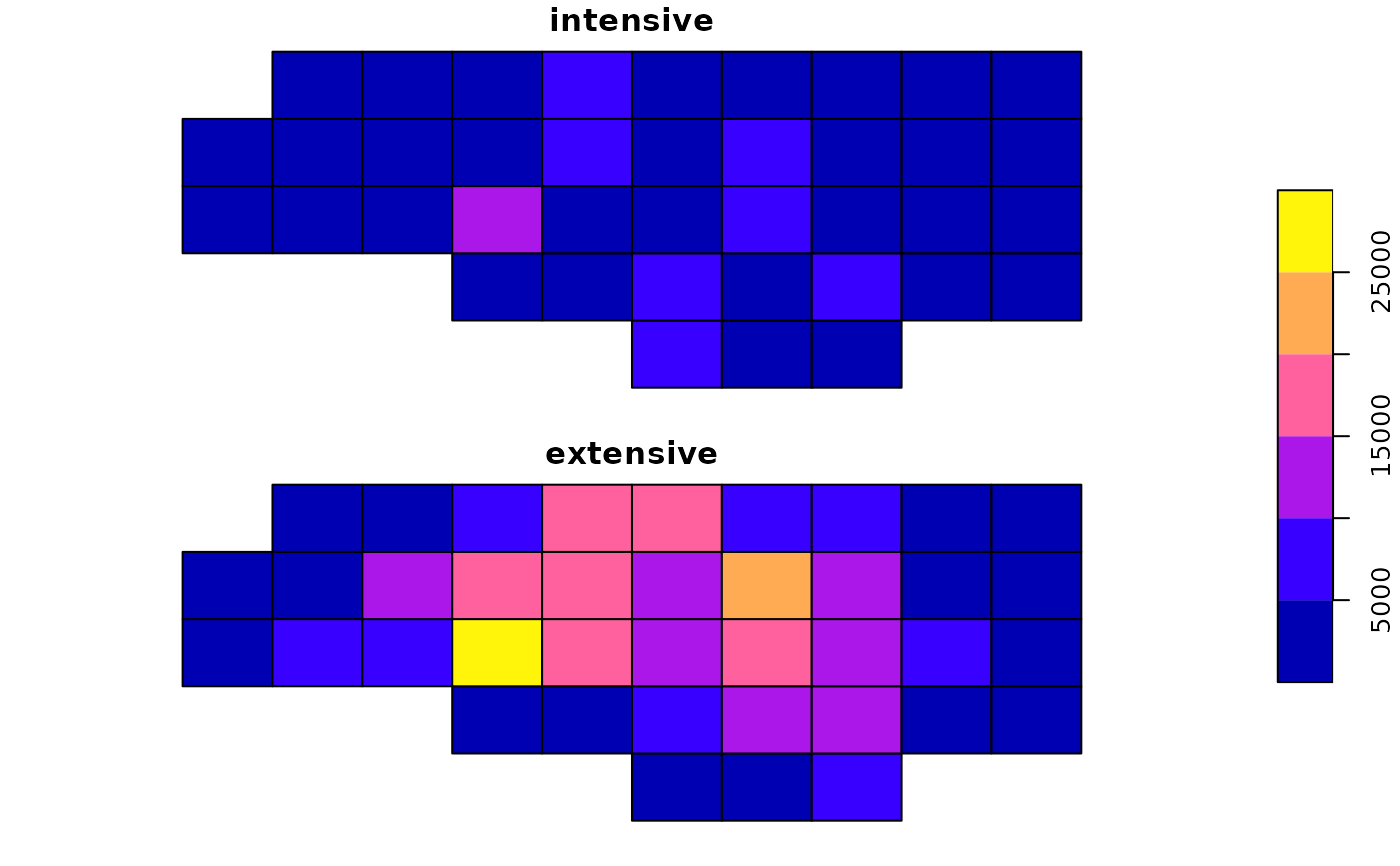
g = st_make_grid(nc, n = c(10, 5))
a1 = st_interpolate_aw(nc["BIR74"], g, extensive = FALSE)
#> Warning: st_interpolate_aw assumes attributes are constant or uniform over areas of x
sum(a1$BIR74) / sum(nc$BIR74) # not close to one: property is assumed spatially intensive
#> [1] 0.4026287
a2 = st_interpolate_aw(nc["BIR74"], g, extensive = TRUE)
#> Warning: st_interpolate_aw assumes attributes are constant or uniform over areas of x
# verify mass preservation (pycnophylactic) property:
sum(a2$BIR74) / sum(nc$BIR74)
#> [1] 0.9999998
a1$intensive = a1$BIR74
a1$extensive = a2$BIR74
plot(a1[c("intensive", "extensive")], key.pos = 4)